Introduction
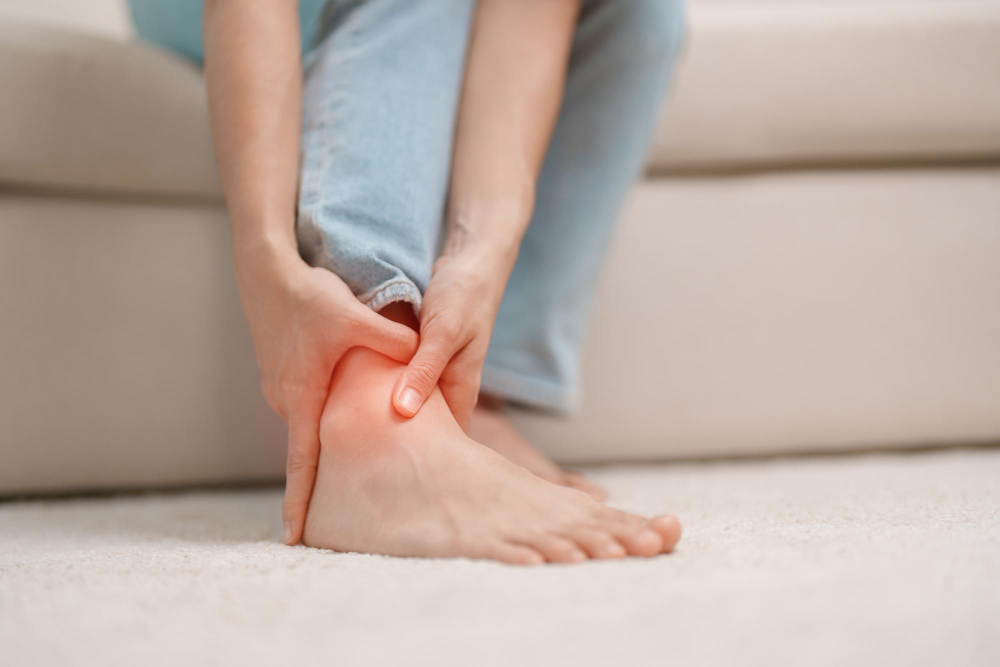
Tendonitis is a common condition that affects many people. It happens when a tendon, which connects muscle to bone, becomes inflamed or irritated. Because tendons help you move, tendonitis can make daily tasks painful. Often, people feel pain, swelling, or stiffness near a joint. In fact, tendonitis can affect your shoulder, elbow, wrist, knee, or ankle. Early care and proper treatment can help you recover faster. This blog explains the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention tips for tendonitis.
Causes of Tendonitis
Many things can lead to tendonitis. Most often, it is caused by overuse or repeating the same motion. For example, playing sports like tennis or golf can strain your tendons. Sometimes, sudden injuries or heavy lifting can also cause tendonitis. In addition, poor posture or not warming up before exercise increases your risk. Age is another factor, as tendons lose flexibility over time. Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or rheumatoid arthritis, may also raise your risk.
Common Symptoms
Tendonitis symptoms can vary, but some signs are very common. Usually, you will feel pain near a joint. The pain may get worse with movement. Swelling, warmth, or redness can also appear. Sometimes, you may notice a lump along the tendon. In severe cases, you might have trouble moving the joint. If you notice these symptoms, it is important to rest and seek advice if they do not improve.
Diagnosis Methods
Doctors use several ways to diagnose tendonitis. First, they will ask about your symptoms and medical history. Next, they will examine the affected area. Sometimes, they may ask you to move the joint to check for pain or weakness. In some cases, imaging tests help confirm the diagnosis. For example, an X-ray can rule out bone problems. An ultrasound or MRI can show swelling or tears in the tendon. These tests help your doctor choose the best tendonitis treatment options for you.
Treatment Options
Tendonitis treatment options depend on how severe your symptoms are. Most people get better with simple self-care steps. However, some may need medical care. Here are common ways to treat tendonitis:
Rarely, surgery may be needed if other treatments do not work. Always follow your doctor’s advice for the best results.
Prevention Tips and Lifestyle Guidance
Preventing tendonitis is possible with a few simple steps. First, always warm up before exercise. Stretching helps keep your tendons flexible. Next, avoid sudden increases in activity. If you play sports, use the right technique and equipment. Take breaks if you do repetitive tasks. In addition, keep your muscles strong with regular exercise. If you have a medical condition, manage it with your doctor’s help. These tips can lower your risk and support healthy joints.
When to See a Doctor
Sometimes, tendonitis can get worse if not treated early. You should see a doctor if:
Early orthopedic care for tendonitis can prevent long-term problems. Therefore, do not wait if your symptoms are severe or last longer than expected.
Conclusion
Tendonitis can affect anyone, but early care and healthy habits make a big difference. If you notice pain or swelling near a joint, take action right away. Simple steps like rest, ice, and gentle exercise can help. However, if symptoms do not improve, seek expert help. Consult an orthopedic specialist for personalized advice on tendonitis.