Introduction
Osteoporosis is a common bone disease that affects millions of people worldwide. In the USA, it is a major health concern, especially for older adults. Because osteoporosis weakens bones, it increases the risk of fractures. Early detection and proper care can help maintain strong bones and prevent serious injuries.
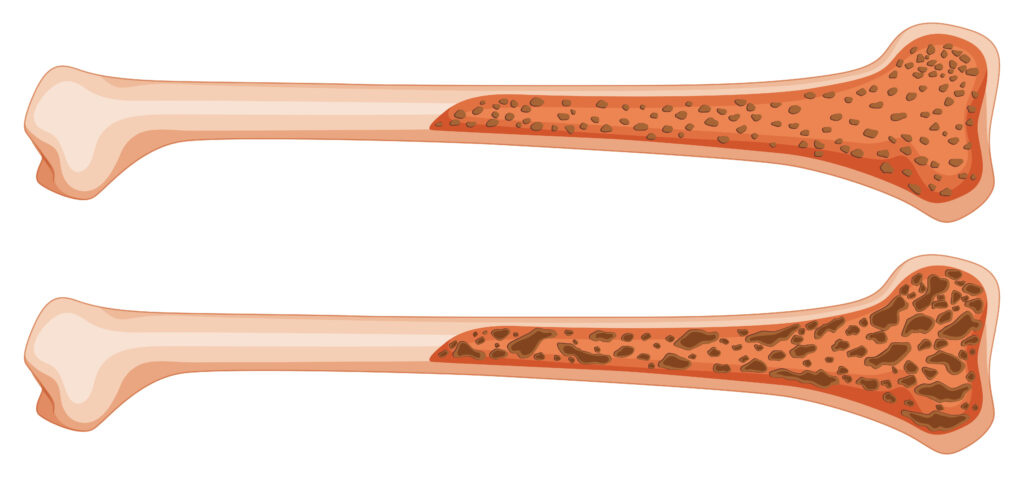
What is Osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis means “porous bone.” In this condition, bones lose strength and become fragile. As a result, even a minor fall or bump can cause a fracture. While anyone can develop osteoporosis, it is more common in women and older adults. Good bone health is important for everyone, so understanding this disease is key.
Causes of Osteoporosis
Several factors can lead to osteoporosis. Some causes are out of your control, but others can be managed. Knowing these risk factors helps you take steps to protect your bones.
Symptoms of Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is often called a “silent disease” because it develops slowly. Usually, there are no symptoms until a bone breaks. However, some signs may appear as the disease progresses.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it is important to talk to your doctor. Early action can help prevent further bone loss.
Diagnosis of Osteoporosis
Doctors use several methods to diagnose osteoporosis. Early diagnosis is important for effective treatment. The most common test is a bone density scan, also called a DEXA scan. This test measures how strong your bones are. In addition, your doctor may ask about your medical history and risk factors. Blood tests may also be used to check calcium and vitamin D levels.
Treatment Options for Osteoporosis
There are many osteoporosis treatment options available. Your doctor will suggest the best plan based on your needs. Treatment aims to slow bone loss, strengthen bones, and prevent fractures.
Always follow your doctor’s advice when starting any treatment.
Lifestyle Tips for Better Bone Health
Healthy habits can make a big difference in managing osteoporosis. Even small changes can help protect your bones.
How to Prevent Osteoporosis
Prevention is the best way to avoid osteoporosis and its complications. While some risk factors cannot be changed, many can be managed with healthy choices.
By following these tips, you can lower your risk and enjoy better bone health.
Conclusion
Osteoporosis is a serious but manageable condition. Because it often has no early symptoms, regular check-ups and healthy habits are important. If you are concerned about your bone health or have risk factors, consult a healthcare specialist for personalized osteoporosis advice.